Unveiling the Mystery of Hyperpigmentation: Causes, Treatments, and a Path to Even-Toned Skin
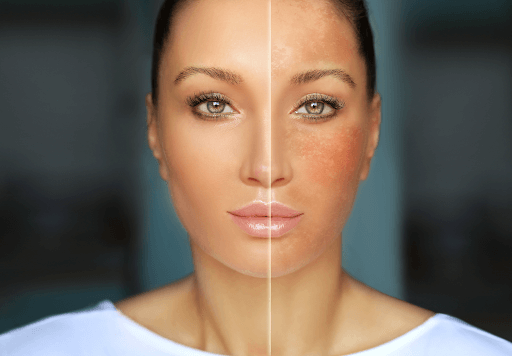
Hyperpigmentation. The word itself can conjure up anxieties about uneven skin tone, dark spots, and a longing for a flawless complexion. But fear not! Hyperpigmentation, while a common skin concern, is treatable and manageable. This comprehensive blog delves deep into the world of hyperpigmentation, exploring its causes, types, effective treatments, and preventative measures.
We’ll unveil the science behind hyperpigmentation, decode the different types that can affect various skin tones, and empower you with knowledge to navigate treatment options and achieve a more even-toned complexion. Whether you’re experiencing a few sunspots or grappling with more prominent hyperpigmentation, this blog is your guide to regaining confidence in your radiant skin.
Demystifying Hyperpigmentation: What Causes Those Dark Spots?
Hyperpigmentation occurs when the skin produces an excess of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. This excess melanin causes patches of skin to become darker than the surrounding area. It’s a prevalent concern across all skin tones, though the appearance and triggers might differ.
Here’s a breakdown of the key factors contributing to hyperpigmentation:
- Melanin Production: Melanin is produced by melanocytes, cells located in the skin’s lower layer (dermis). Several factors can stimulate melanin production, leading to hyperpigmentation.
- Sun Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun are a prime culprit. UV rays trigger melanocytes to produce more melanin in an attempt to protect the skin from sun damage. This can lead to sunspots, freckles, and uneven pigmentation.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly estrogen and progesterone, can stimulate melanin production. This is why hyperpigmentation is common during pregnancy (melasma) and menopause.
- Inflammation: Skin injuries, acne, and inflammatory skin conditions like eczema can trigger melanin production at the site of inflammation, leading to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH).
- Certain Medications: Some medications, like birth control pills and certain antibiotics, can increase sun sensitivity and make hyperpigmentation more likely.
A Spectrum of Hyperpigmentation: Different Types and Their Characteristics
Hyperpigmentation manifests in various forms, each with its unique triggers and treatment approaches. Here’s a closer look at some common types:
- Melasma: Also known as “the mask of pregnancy,” melasma presents as brown or grayish patches on the face, often symmetrical across the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip. Hormonal changes are the primary trigger, making it prevalent during pregnancy and menopause.
- Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): This type arises after inflammation in the skin heals. Acne, eczema, and other skin conditions can leave dark spots in their wake. PIH is more common in people with darker skin tones.
- Sunspots (Solar Lentigines): These small, flat brown spots are caused by chronic sun exposure and typically appear on areas exposed to the sun, like the face, hands, and arms.
- Freckles: These small, light brown to tan spots are clusters of melanin and are often genetic. They are more common in people with fair skin and tend to become darker with sun exposure.
- Periorbital Hyperpigmentation: Dark circles under the eyes can be caused by various factors, including genetics, allergies, sun damage, and fatigue.
Understanding the specific type of hyperpigmentation you’re experiencing is crucial for selecting the most effective treatment approach. Consulting a dermatologist can help with an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Unveiling the Treatment Arsenal: Combating Hyperpigmentation
The good news? Hyperpigmentation is treatable. Here’s an overview of common treatment options offered by dermatologists or available over-the-counter:
- Topical Treatments: Products containing ingredients like hydroquinone, kojic acid, azelaic acid, and licorice root can lighten hyperpigmentation by inhibiting melanin production and promoting cell turnover.
- Chemical Peels: These treatments remove the outer layer of skin, revealing a smoother, more even-toned appearance. The strength of the peel determines the depth of treatment and resulting downtime.
- Microneedling: This minimally invasive procedure uses tiny needles to create microscopic injuries in the skin. This triggers the skin’s healing process, promoting collagen production and reducing the appearance of hyperpigmentation.
- Laser Treatments: Different types of lasers target melanin and break it down, fading dark spots and promoting a more even skin tone.
- Light Therapy: Intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy uses broad-spectrum light to target melanin and reduce hyperpigmentation.
Conclusion
From its causes and triggers, to a range of effective treatments, this blog provides a comprehensive overview of hyperpigmentation. By unraveling the science behind hyperpigmentation and exploring its various types, readers are equipped with valuable knowledge to address this common skin concern. Whether seeking to combat sunspots, melasma, or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, individuals can navigate treatment options with confidence, paving the way towards achieving a more even-toned and radiant complexion.
